Date: 5 August 2014
Pt SD congestive heart failure 5 images
Copyright:
FIT
Notes:
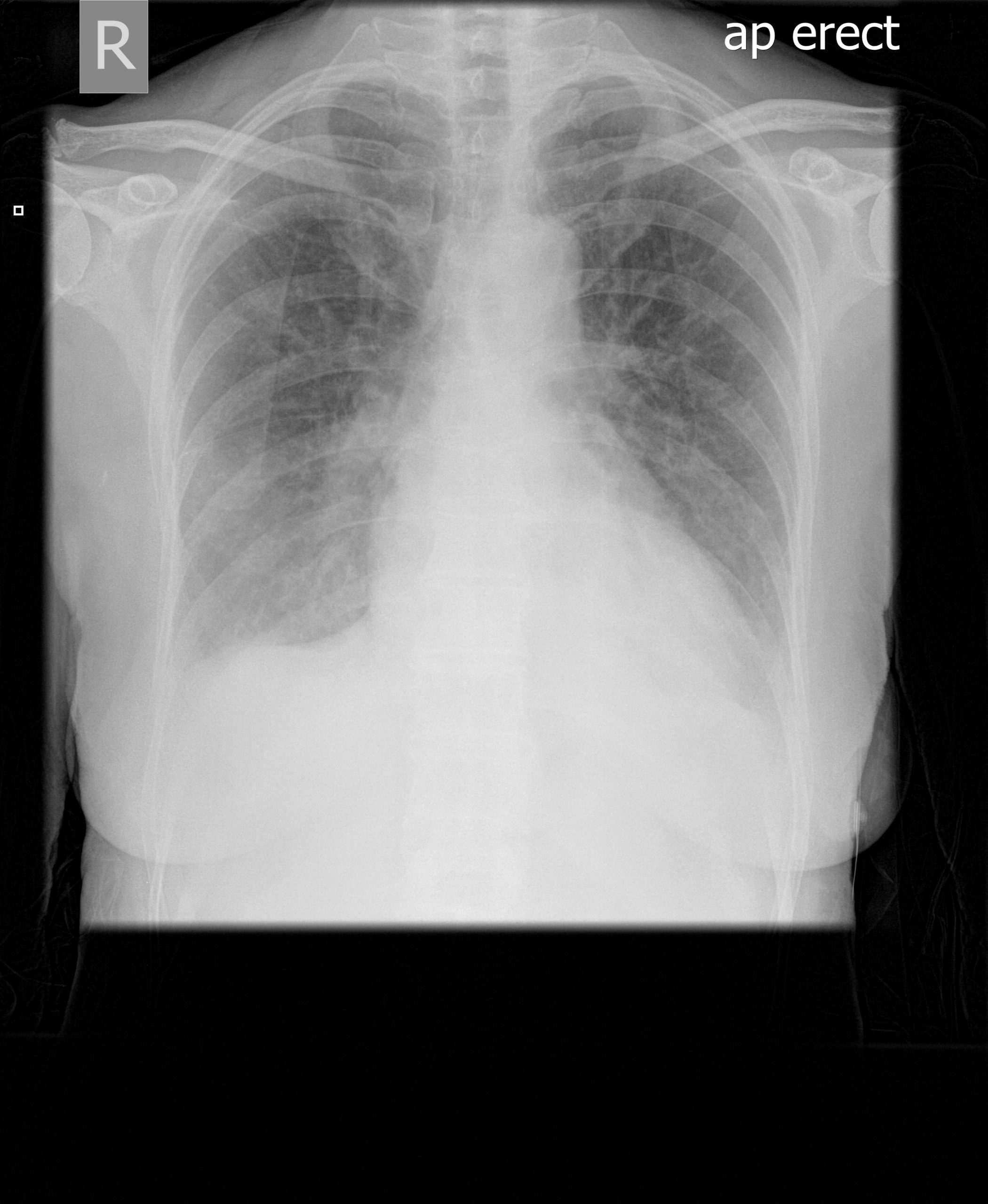
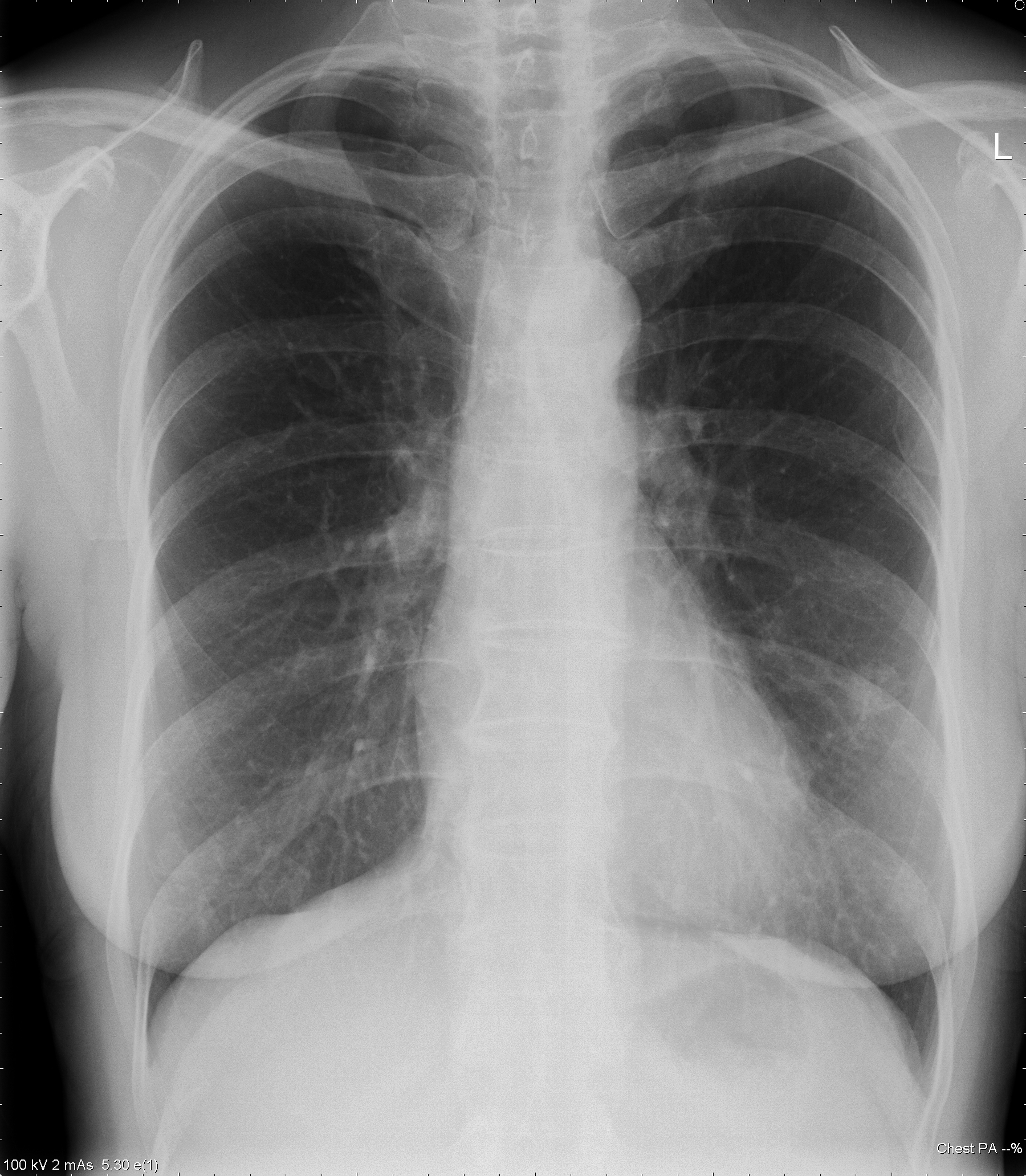
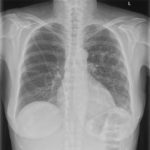
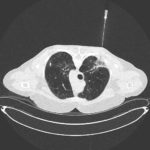
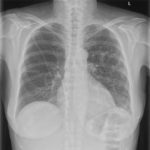
This 63 year old woman with a lung nodule, probably caused by Aspergillus, was treated with itraconazole 300mg daily. After 3 weeks, she noticed dizziness and her blood pressure was reduced at 100/60. A week later, she was complaining of headaches, feeling unwell and fluctuating blood pressure. Her BP was 133/62 and pulse 90/min and regular. Her thyroid replacement therapy was excessive and so reduced, as was her itraconazole dose, although subsequent itraconazole levels were in the therapeutic range. Six days later she was admitted to hospital very breathless with bilateral pleural effusions. Itraconazole was stopped.
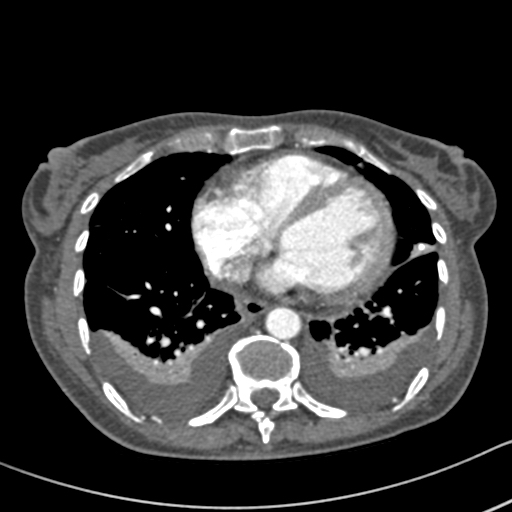
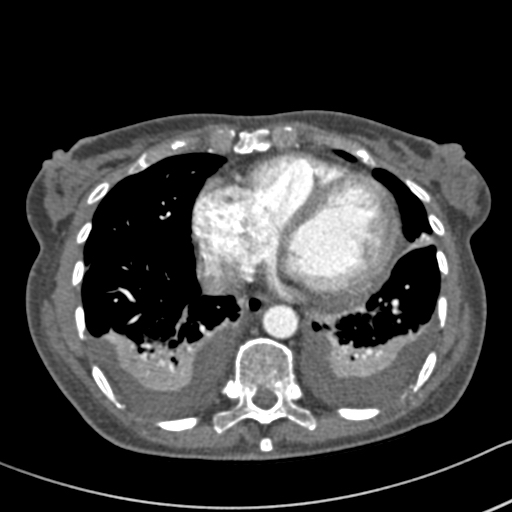
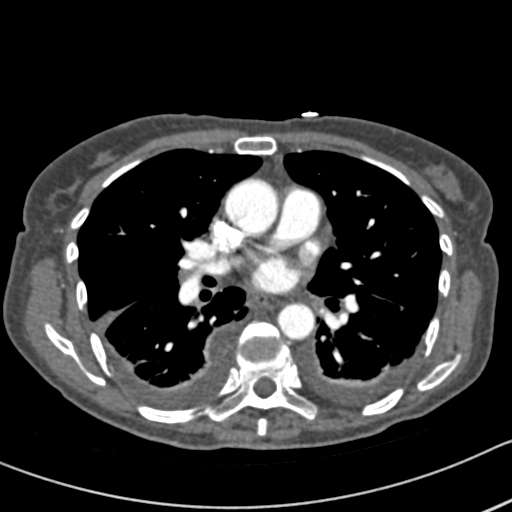
Her CXR shows bilateral effusions, probable cardiac enlargement and some upper lobe vessel fullness in the lungs. The CT scan confirms bilateral flexural effusions, with associated consolidated lung and fluid in the fissure on the right. The heart is enlarged and right ventricle dilated. In May, all had resolved and she is left with a nodule in the left lower lobe.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
PtDS2 –Repeated chest infections arrested by itraconazole therapy in ABPA and bronchiectasis
DS2 developed asthma age 24 and now aged 62. From about age 30 she started getting repeated chest infections and a few years later ABPA and bronchiectasis was diagnosed. Infections continued requiring multiple courses of antibiotics annually. At one point DS2 developed a pneumothorax, possibly because of excess coughing. She has chronic rhinitis and mannose binding lectin deficiency. In May 2011, she started itraconazole therapy, and has needed no antibiotic courses for her chest since. Her rhinitis with sinusitis occasionally bothers her. She is delighted to have gone 18 months with no chest infections.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
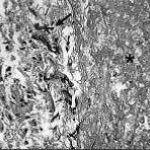
Aspergillus hyphae (arrow) in the lumen without invasion of the necrotic bronchial wall (*) (Nicod 2001).
-
fibrinonecrotic material (arrow) from the airway shown in A, with subocclusion of the bronchial lumen (*)
-
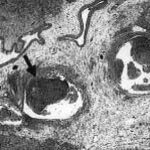
Fibrinous or pseudomembranous bronchitis (arrow) with subocclusion of the airways (* indicates subocclusion of the airways by pseudomembranes)

-
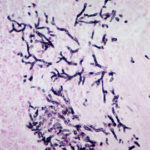
Bronchoscopic biopsy demonstrated septate hyphae with branching at 45o (methenamine silver stain ×400).