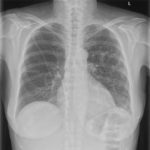
Date: 26 November 2013
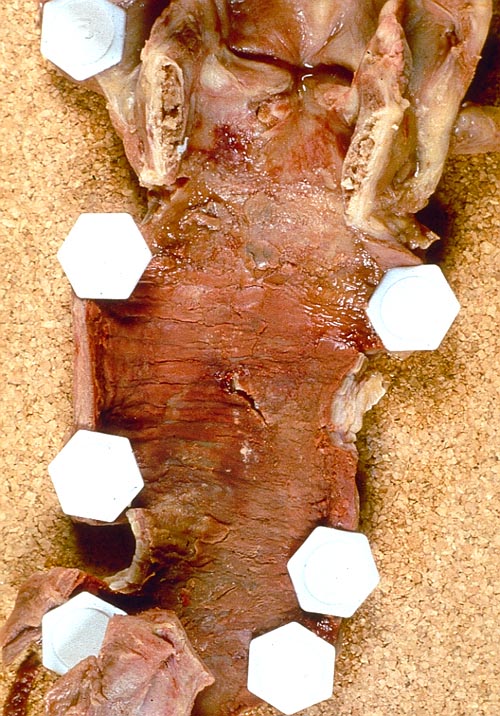
Pt FT. Autopsy appearance of the trachea, after the adherent pseudomembrane had been removed, revealing confluent ulceration superiorly with small green plaques of Aspergillus growth on the trachea inferiorly.
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
This patient had an acute onset of neutropenia, of undetermined origin, which was treated with prednisolone, before developing rapidly progressive and ultimately fatal pseudomembranous Aspergillus tracheobronchitis. His case was reported because he developed a unilateral monophonic wheeze, which prompted a diagnostic bronchoscopy.Tait RC, O’Driscoll BR, Denning DW. Unilateral wheeze due to pseudomembranous Aspergillus tracheobronchitis in the immunocompromised patient. Thorax 1993; 48: 1285-1287. Disseminated aspergillosis was found at autopsy and cultures from each organ were found to be clonal (Birch M, Nolard N, Shankland G, Denning DW. DNA typing of epidemiologically-related isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Epidemiol 1995; 114: 161-168.)
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
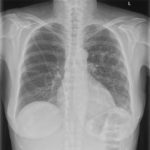
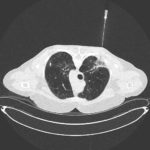
PtDS2 –Repeated chest infections arrested by itraconazole therapy in ABPA and bronchiectasis
DS2 developed asthma age 24 and now aged 62. From about age 30 she started getting repeated chest infections and a few years later ABPA and bronchiectasis was diagnosed. Infections continued requiring multiple courses of antibiotics annually. At one point DS2 developed a pneumothorax, possibly because of excess coughing. She has chronic rhinitis and mannose binding lectin deficiency. In May 2011, she started itraconazole therapy, and has needed no antibiotic courses for her chest since. Her rhinitis with sinusitis occasionally bothers her. She is delighted to have gone 18 months with no chest infections.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
Aspergillus hyphae (arrow) in the lumen without invasion of the necrotic bronchial wall (*) (Nicod 2001).
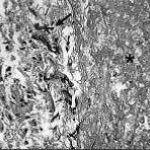
-
fibrinonecrotic material (arrow) from the airway shown in A, with subocclusion of the bronchial lumen (*)
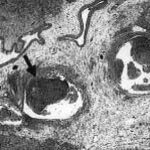
-
Fibrinous or pseudomembranous bronchitis (arrow) with subocclusion of the airways (* indicates subocclusion of the airways by pseudomembranes)

-
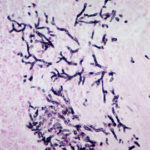
Bronchoscopic biopsy demonstrated septate hyphae with branching at 45o (methenamine silver stain ×400).