Date: 26 November 2013
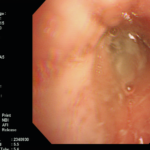
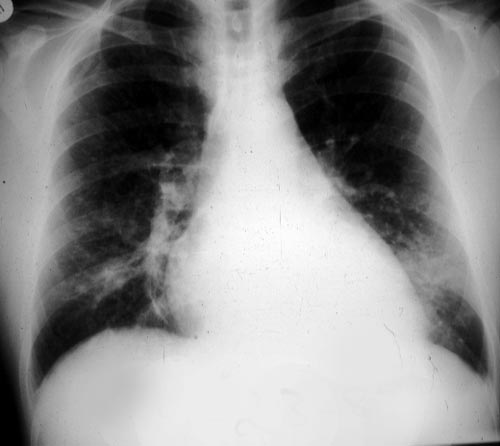
The patient was a 37-year old man in whom P.carinii pneumonia developed in August 1987, followed by esophageal candidiasis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding in September. Chronic perineal herpes led to the formation of rectourethral fistula and multiple episodes of urosepsis, for which he was given long-term ciprofloxacin therapy to suppress bacterial colonization of the bladder. He discontinued heavy alcohol use in September 1987 and smoked marijuana occasionally.On April 23 1989, the patient was admitted to the hospital with a two-month history of increasing dry cough with shortness of breath. He reported transient fever (temperature to 41°C). He was admitted with leukopenia, with his neutrophil count falling to 16 x 106/l on the second hospital day. A chest film showed bilateral fluffy lower-lobe infiltrates (this image). Zidovudine was discontinued. The patient had a rapidly downhill course despite intravenous treatment with trimethioprim-sulfamethoxazole. A bronchoscopy on the sixth hospital day revealed what appeared to be a foreign body in the left lower-lobe bronchus. It was removed, together with much necrotic, mucoid debris. On microscopic examination, the “foreign body” was necrotic, containing large numbers of hyphae and conidia in a manner typical of an aspegilloma or fungal cast. The culture grew A.fumigatus.
Clinical and radiologic improvement followed bronchoscopy, and itraconazole therapy was begun because of the concern about invasive aspergillosis in the setting of marked neutropenia. The patient tolerated the medication well at a dose of 200 mg twice daily, and the chest film became normal over the subsequent six weeks, after which itraconazole was discontinued. A sputum specimen cultured for fungus four weeks after the start of therapy was negative. After the initial improvement with itraconazole, the patient had recurrent urosepsis, associated with dehydration and marked confusion. Nine weeks after the discontinuation of itraconazole, he died of progressive dementia complicated by recurrent pneumonia and sepsis. There was no postmortem examination.
This patient was described (pt 11) and this chest radiograph reproduced in Denning DW, Follansbee S, Scolaro M, Norris S, Edelstein D, Stevens DA. Pulmonary Aspergillosis in the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 654-662.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
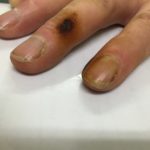
Patient with chronic productive cough, chest pain and ABPA, unable to take itraconazole or nebulised amphotericin B. Smokes at least 40 roll up cigarettes a day.
 ,
, 
-
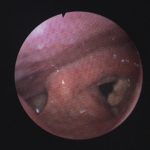
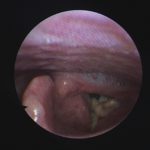
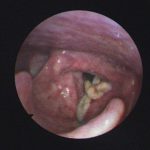
Laryngeal aspergillosis, probably related to inhaled corticosteroids.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
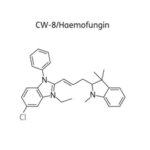
VL-2397 (formerly known as ASP2397) is a novel antifungal drug initially developed by our partner, Astellas Pharma. This drug was isolated from a leaf litter fungus Acremonium species collected in a Malaysian national park. Astellas presented two posters at the 2014 ICAAC meeting which described the in vitro and the in vivo antifungal activities of this drug. The differentiating attributes from the preclinical data of VL-2397 include:
- A novel mechanism of action, with a potential to be complementary or synergistic with the existing classes of antifungals.
- Rapid fungal cell kill activity demonstrated in preclinical models, which was faster than marketed antifungals.
- Activity against azole-resistant fungal species.
- Low propensity for P450 drug-drug interactions.
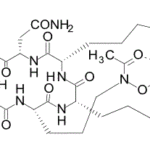
-
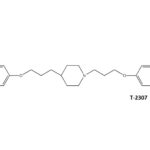
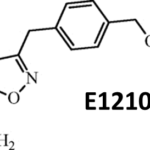
SCY-078, new orally available beta-1,3-d-glucan synthase inhibitor, Formely MK-3118.
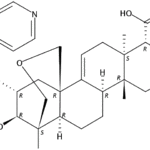
-
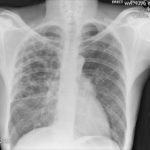
Pt DSM Community acquired primary Aspergillus pneumonia. Two x-rays taken on 02/02/2010 then 05/03/2010
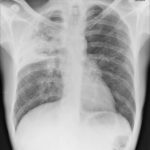 ,
, 


 ,
,