Date: 21 January 2014
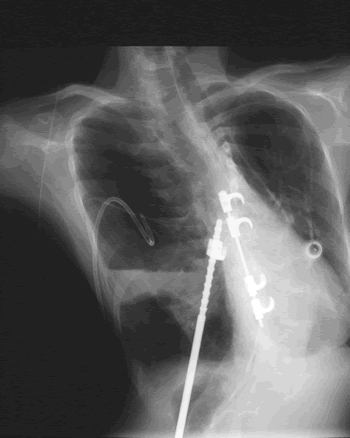
The chest is distorted by a deformity of the back and ribs.
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
This patient’s X-ray is complex. The chest is distorted by a deformity of the back and ribs. Substantial metalwork following a spinal fusion is in place to support the vertebral column and part of this overlies the heart and part of it crosses the left lung. The patient also has a portacath device in-situ over the right lung, which allows i.v. antibiotics to be given. A needle is in-situ inside the portacath device. An external drainage tube is currently in-situ in a large air cavity and left upper thorax. This cavity contains mostly air but there is some fluid with the fluid level at its base. Underneath this large pyopneumothorax is a normal component of left lower lobe. The heart is very substantially moved to the right of the lung because of a previous right lower lobe resection. There is no evidence of aspergillosis on this x-ray as it stands.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
25/04/90 After itraconazole treatment. Major improvement, defined as a complete response, after 10 weeks therapy with itraconazole.
-
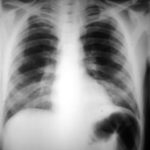
Image A. Chest x-ray shows a single nodule in the left mid lung field.
Image B. This emphasises how chest x-rays in this context underestimate the extent of disease. The most anterior nodule has ground glass surrrounding the nodule, a halo sign. This diagnostic feature is missed on plain chest X-rays.
 ,
, 
-
Chest X ray after 4 days, prior to treatment, showing massive increase in volume of lesion (Fig 2)
-
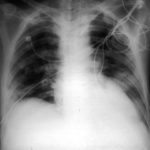
Image A. This patient, aged 25 years developed a non productive cough and dyspnoea in the context of late-stage AIDS, CMV disease with ganciclovir-induced neutropenia and receiving corticosteroids. His chest radiograph shows fine bilateral reticular lower-lobe shadowing. He then developed gastro-intestinal bleeding with a gastric ulcer which showed hyphae on biopsy. He then developed blindness of one eye and the globe of his eye perforated. Hyphae were seen and Aspergillus cultured from the vitreous aspirate.
Image B. This radiograph, taken 25 days after the first and 3 days before death, shows of fine bilateral lower-lobe reticular shadows progressing to nodules in all lung zones.
This patient was reported as patient 3 in Denning DW, Follansbee S, Scolaro M, Norris S, Edelstein D, Stevens DA. Pulmonary aspergillosis in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 654-662.
 ,
, 
-
Further details
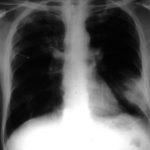
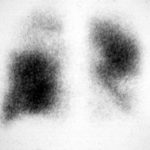
Image A. Bronchoscopy revealed Aspergillus on culture.
Image B. The ability of Aspergillus to cause pulmonary infarction, probably through direct angioinvasion in this case, is characteristic.
 ,
, 
-
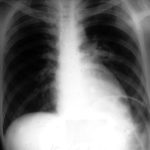
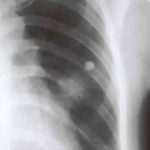
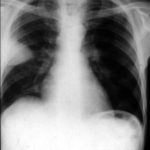
(Fig 1) Chest radiograph with ‘classical’ appearance of a pulmonary infarction – a wedge-shaped lesion peripherally set against the pleura.
-
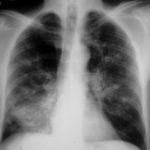
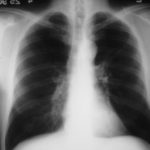
Large soft left upper-lobe shadow of focal invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in leukaemia, that was missed on earlier radiographs but apparent retrospectively. Variable density of the lesion suggests cavitation, which would be clearly visible on a CT scan of the thorax.
-
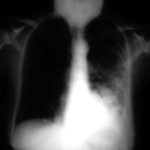
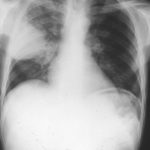
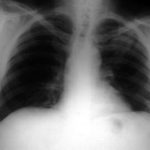
Severe unilateral invasive aspergillosis of the left lung, with complete consolidation of the left lower-lobe and reticular shadowing extending up into the left upper lobe. The right lung appears normal.