Date: 26 November 2013
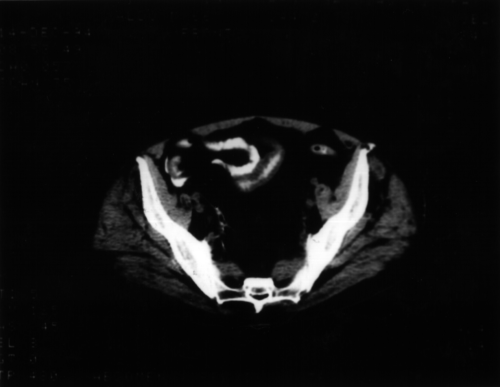
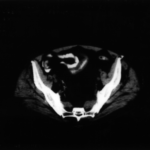
Intestinal aspergillosis. A CT scan showing intestinal aspergillosis
Copyright:
Courtesy of Dr. Maria Cecilia Dignani, MD, from Fundaleu, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus can produce aflatoxins are generally known as storage fungi, but they can also cause ear rots in the field. These species are observed as a gray-green, powdery molds and they can be detected in corn because they produce compounds that are fluorescent under black light.

-
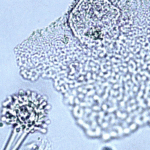
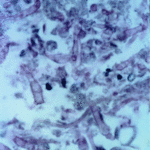
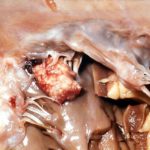
Histopathology of the jejenum showing necrosis and hyphae consistent with Aspergillus
-
Further image details
Image A. Multiple small lesions at both ends of the cordae tendinae in this patient who died of disseminated aspergillosis. He was a previously well 70 year old man who developed pneumonia on holiday, required artificial ventilation and died with a rapidly progressive cavitating pneumonia. Autopsy showed disseminated aspergillosis.
Image B. Another lesion in pt DB, that histologically showed a mass of hyphae and fibrin.
Image C. Large destructive lesion on the mitral valve in patient DB.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
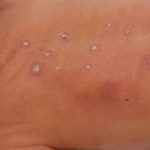
The patient was a 610 g twin male born by spontaneous normal vaginal delivery at 23 weeks and 4 days gestation. He was started on benzyl penicillin and gentamicin for sepsis. On day 3, he developed metabolic acidosis, hyponatremia, anemia, thrombocytopenia and jaundice and his antibiotics were changed to vancomycin, cefotaxime and fluconazole.
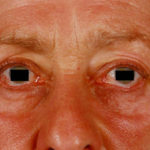
On day 10, multiple circular skin papules with white eschars were noted on his back (Figure A). A full septic screen was repeated including skin scraping and biopsy for urgent microscopy and culture. Microscopy of skin scrapes revealed fungal elements including hyphae and fruiting heads suggestive of Aspergillus spp (Figure B). Lipid amphotericin B was commenced and fluconazole was stopped. Skin scrapings on culture grew Aspergillus fumigatus. A diagnosis of primary cutaneous aspergillosis was made. The patient responded to oral posaconazole 6mg/kg/8 hourly. All lesions disappeared after 44 days and he continued with posaconazole until day 60.
Published case at Langan et al Pediatr Dermatol 2010 Jul-Aug 27 (4) 403-4
 ,
,