Date: 26 November 2013
Further details
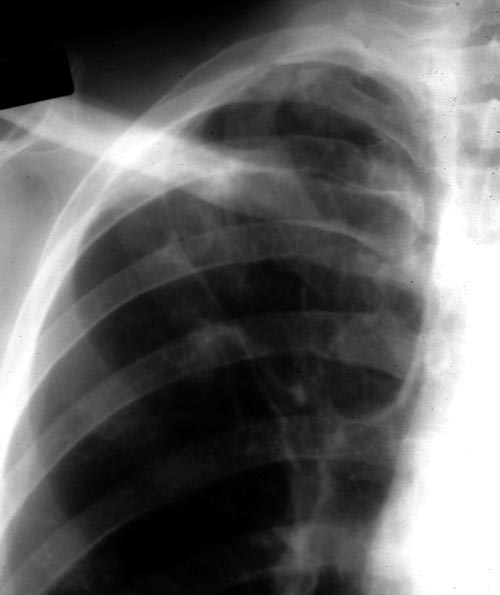
Image A. December 1991. The lesions were considered to be possibly malignant and surgically resected. Histological examination showed granulomata containing hyphae consistent with Aspergillus. Fungal cultures were not done.
Image B. June 1992 Despite resection of part of the right upper-lobe, invasive aspergillosis recurred six months later. Sputum cultures grew A.fumigatus and Aspergillus antibodies were detected in serum. He responded to itraconazole but subsequently progressed.
Image C. September 1992 Although the appearance suggests the formation of aspergillomas, the contemporaneous CT scan did not confirm this.
Image K. December 1991. There are no particular distinguishing characteristics of invasive aspergillosis. The right upper-lobe was resected and histological examination showed granulomata containing hyphae consistent with Aspergillus. Fungal cultures were not done.
Image M & N. CT scan of thorax. Post RVL segmentectomy with chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. CT shows patchy consolidation with cavitation in the apical segment of right lower lobe. A tiny pneumothorax can be identified posterolaterally (arrows).
Image O. Reference: Muco-cutaneous retinoid effects and facial erythema related to the novel triazole antifungal agent voriconazole. Denning, DW & Griffiths, CEM. Clin.Exp Dermatol 2001, 26(8), 648-53.
Copyright:
Courtesy of Dr D Denning, Wythenshawe Hospital, Manchester.(© Fungal Research Trust)
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend