Date: 26 November 2013
This recording of peak flow was taken prior to and during the first 4 weeks of inhaled steroids (Becotide 100 and Duovent both 2 puffs 4x daily). The patient had had asthma since age 4, and been treated with bronchodilators and oral courses of steroids when severely affected. The chart, which the patient completed at home, shows that early in week one her peak flow varied from 200-250 L/min. As the medication started to work, the peak flows gradually increased to reach 360-420 L/min in the 4th week. The lower value each morning is characteristic of asthma.
The response to steroids is important confirmation of the diagnosis of asthma (reversible airways obstruction). Many years later she developed ABPA, while on inhaled steroids, with severe upper lobe central bronchiectasis, an IgE of 6,800 Kiu/L, positive aspergillus precipitins, an Aspergillus RAST of 58.7KUa/L (normal <0.4) and eosinophilia.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Left= an agar air plate exposed for 2 minutes after the barley had been turned. showing numerous colonies of the fungus following incubation at 26C on 2% malt agar.Right= A sputum sample taken from a maltworker after exposure showing many fungal colonies when cultured on agar. His commensal yeast flora is seen towards the right base as cream/white colonies.

-
growing on contaminated barley malt. The deep blue-green heads made up of chains of conidia are seen on the left. On the right, conidiophores from which conidial chains are developed show typical clavate heads. Stain- Cotton blue in Lactophenol.

-
Sections of colonised alveoli
On the left, the conidiophores sporulate freely, on the right they are seen to cease development at the phialide stage. Carbon deposits are clearly seen here.A=alveolus, As=alveolar septum, C=conidiophore, P=phialide
-
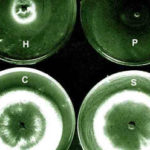
The growth isolated from the aspergilloma in the presence of living cells of the three bacterial species in culture.The most marked inhibition occurred with Pseudomonas aeruginosa(P) and Haemophilus influenzae(H) and to a much lesser extent with Staphylococcus aureus(S). C=control. Inhibitory factors were components of the bacterial slime layers.
-
aspergilloma removed from the lung cavity seen in section.Staining was with methenamine/silver and light green. The structure shows zonation probably due to variations in the growth rate of mycelium(deep brown). A mucus layer(stained green) containing cell debris and bacteria is seen shrouding the fungus. Bacterial genera were Staphylococcus, Haemophilus and Pseudodomonas.

-
Plugs cultured on agarA young colony of the fungus(AF) has a central patch of sporulation and is surrounded by colonies of bacteria and yeasts.

-
A part of the mycelium in a stained sputum plug showing the dichotomously branched hyphae of Aspergillus fumigatus.