Date: 26 November 2013
This recording of peak flow was taken prior to and during the first 4 weeks of inhaled steroids (Becotide 100 and Duovent both 2 puffs 4x daily). The patient had had asthma since age 4, and been treated with bronchodilators and oral courses of steroids when severely affected. The chart, which the patient completed at home, shows that early in week one her peak flow varied from 200-250 L/min. As the medication started to work, the peak flows gradually increased to reach 360-420 L/min in the 4th week. The lower value each morning is characteristic of asthma.
The response to steroids is important confirmation of the diagnosis of asthma (reversible airways obstruction). Many years later she developed ABPA, while on inhaled steroids, with severe upper lobe central bronchiectasis, an IgE of 6,800 Kiu/L, positive aspergillus precipitins, an Aspergillus RAST of 58.7KUa/L (normal <0.4) and eosinophilia.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Itraconazole rash – macropopular rash after 7 days treatment with Itraconazole, in a patient with AIDS
-
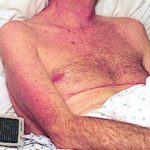
A 72 year-old male patient had been in treatment for many years for severe asthma with relatively good exercise tolerance. Over the past two years he had increasing problems of shortness of breath, cough and productive sputum. There was no history of chest pain, haemoptysis or fever. His total IgE was 680.0 IU/l, and specific IgE against Aspergillus fumigatus was 14.6 IU/l. Precipitins against A. fumigatus were weakly positive (titre 1/2), and there was no eosinophilia. Computed tomography revealed marked emphysema but only mild bronchiectasis. Based on these results he was diagnosed with severe asthma with fungal sensitisation (SAFS) and itraconazole was started (SporanoxTM 200mg bds). Itraconazole dosage was reduced to 200 mg daily one month later due to progressive bilateral ankle oedema. Itraconazole levels by bioassay were 17.5 mg/l at that time (normal range 5-15 mg/l). Despite showing improvement on his chest symptoms, peripheral oedema became a major negative impact on patient’s quality of life. There were no signs of heart failure. Figure 1 was taken 2 months after itraconazole was started, when drug levels were 9.8 mg/l. Itraconazole was replaced by voriconazole. Concomitant medications included furosemide (80 mg daily) and spironolactone (100 mg daily). After discontinuing itraconazole, the oedema quickly subsided.
Ankle oedema is an uncommon complication of therapy with itraconazole. It has occurred in about 4% of patients treated in clinical trials involving this drug. This complication seems to be more frequent in patients concomitantly receiving calcium channel blockers, which was not the case for our patient. The mechanism is unknown. It usually does not represent cardiac failure, another reported side effect of itraconazole, but this must be excluded. Marked oedema requiring drug suspension is a rare phenomenon, and has not been previously reported in association with itraconazole.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
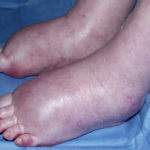
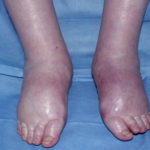
The insert shows the size of the discs. These discs dissociate after infusion to release amphotericin B preferentially into the reticuloendothelial system and lung. This form of amphotericin B is marketed as either Amphotec or Amphocil, depending on the country.