Date: 26 November 2013
Aspergillus terreus Thom. Conidial head of Aspergillus terreus. Conidial heads are compact, columnar and biseriate. Conidiophores are hyaline to slightly yellow and smooth walled.
Copyright:
With thanks to G Kaminski. D Ellis and R Hermanis Mycology Unit, Women’s & Children’s Hospital , Adelaide, South Australia 5006
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 40-50 mm diam, plane, low and velutinous, usually quite dense; mycelium white; conidial production heavy, brown (Dark Blonde to Camel, 5-6D4); reverse pale to dull brown or yellow brown. Colonies on MEA 40-60 mm diam, similar to those on CYA or less dense. Colonies on G25N 18-22 mm diam, plane or irregularly wrinkled, low and sparse; conidial production light, pale brown; brown soluble pigment sometimes produced; reverse brown. No growth at 5°C. Colonies at 37°C growing very rapidly, 50 mm or more diam, of similar appearance to those on CYA at 25°C.Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, stipes 100-250 μm long, smooth walled; vesicles 15-20 μm diam, fertile over the upper hemisphere, with densely packed, short, narrow metulae and phialides, both 5-8 μm long; conidia spherical, very small, 1.8-2.5 μm diam, smooth walled, at maturity borne in long, well defined columns.Distinctive featuresVelutinous colonies formed at both 25°C and 37°C, uniformly brown, with no other colouration, and minute conidia borne in long columns make Aspergillus terreus a distinctive species.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
5 sputum samples were positive for A. niger, a bronchoscopy was normal and culture and microscopy were negative. Rx voriconazole, 200mg bd was given. An excellent clinical response was seen.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
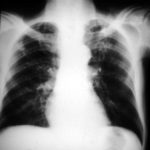
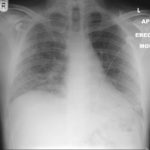
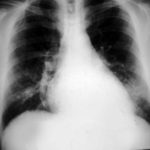
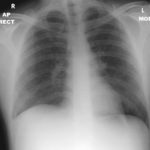
The patient was a 37-year old man in whom P.carinii pneumonia developed in August 1987, followed by esophageal candidiasis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding in September. Chronic perineal herpes led to the formation of rectourethral fistula and multiple episodes of urosepsis, for which he was given long-term ciprofloxacin therapy to suppress bacterial colonization of the bladder. He discontinued heavy alcohol use in September 1987 and smoked marijuana occasionally.On April 23 1989, the patient was admitted to the hospital with a two-month history of increasing dry cough with shortness of breath. He reported transient fever (temperature to 41°C). He was admitted with leukopenia, with his neutrophil count falling to 16 x 106/l on the second hospital day. A chest film showed bilateral fluffy lower-lobe infiltrates (this image). Zidovudine was discontinued. The patient had a rapidly downhill course despite intravenous treatment with trimethioprim-sulfamethoxazole. A bronchoscopy on the sixth hospital day revealed what appeared to be a foreign body in the left lower-lobe bronchus. It was removed, together with much necrotic, mucoid debris. On microscopic examination, the “foreign body” was necrotic, containing large numbers of hyphae and conidia in a manner typical of an aspegilloma or fungal cast. The culture grew A.fumigatus.
Clinical and radiologic improvement followed bronchoscopy, and itraconazole therapy was begun because of the concern about invasive aspergillosis in the setting of marked neutropenia. The patient tolerated the medication well at a dose of 200 mg twice daily, and the chest film became normal over the subsequent six weeks, after which itraconazole was discontinued. A sputum specimen cultured for fungus four weeks after the start of therapy was negative. After the initial improvement with itraconazole, the patient had recurrent urosepsis, associated with dehydration and marked confusion. Nine weeks after the discontinuation of itraconazole, he died of progressive dementia complicated by recurrent pneumonia and sepsis. There was no postmortem examination.
This patient was described (pt 11) and this chest radiograph reproduced in Denning DW, Follansbee S, Scolaro M, Norris S, Edelstein D, Stevens DA. Pulmonary Aspergillosis in the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 654-662.
 ,
, 
-
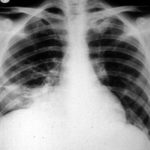
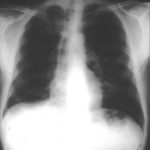
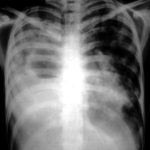
Image A. This 25 year old woman was previously well and presented with a pneumonia of uncertain aetiology. She has infiltrates in right upper-lobe and left middle and lower zones. The diagnosis was later made of chronic invasive pulmonary aspergillosis by bronchoscopy . Subsequently she was diagnosed with adult-onset chronic granulomatous disease with neutrophil function assays.
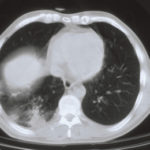
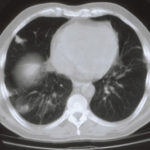
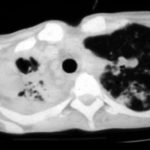
Image B. CT scan of the thorax just below the carina, showing almost complete opacification of the right lung and marked nodular shadowing around the hilum of the left lung.
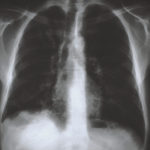
Image C. Progression of pulmonary infiltrates are seen seven weeks later, despite administration of amphotericin B.
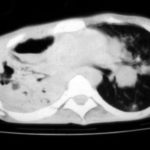
Image D. CT scan of the thorax above the carina showing near complete opacification of the right lung and multiple discrete nodular shadows in the left lung.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
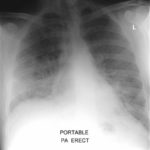
02/10/09 X -ray shows improvement in appearances from initial presentation with complete chest radiographic resolution by 07/11/2008
-
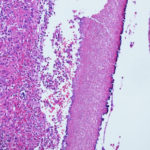
Subacute IPA in rhematoid nodules of the lung. in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Histology sections stained with H&E