Date: 7 May 2013
A four day A. fumigatus culture on malt extract agar (above). Light microscopy pictures are taken at 1000x mag., stained with lacto-phenol cotton blue (right).
Copyright:
With thanks to Niall Hamilton.
Notes:
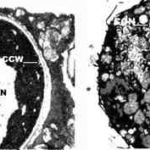
Colonies on CYA 40-60 mm diam, plane or lightly wrinkled, low, dense and velutinous or with a sparse, floccose overgrowth; mycelium inconspicuous, white; conidial heads borne in a continuous, densely packed layer, Greyish Turquoise to Dark Turquoise (24-25E-F5); clear exudate sometimes produced in small amounts; reverse pale or greenish. Colonies on MEA 40-60 mm diam, similar to those on CYA but less dense and with conidia in duller colours (24-25E-F3); reverse uncoloured or greyish. Colonies on G25N less than 10 mm diam, sometimes only germination, of white mycelium. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies covering the available area, i.e. a whole Petri dish in 2 days from a single point inoculum, of similar appearance to those on CYA at 25°C, but with conidial columns longer and conidia darker, greenish grey to pure grey.
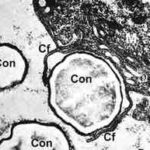
Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, stipes 200-400 µm long, sometimes sinuous, with colourless, thin, smooth walls, enlarging gradually into pyriform vesicles; vesicles 20-30 µm diam, fertile over half or more of the enlarged area, bearing phialides only, the lateral ones characteristically bent so that the tips are approximately parallel to the stipe axis; phialides crowded, 6-8 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, 2.5-3.0 µm diam, with finely roughened or spinose walls, forming radiate heads at first, then well defined columns of conidia.
Distinctive features
This distinctive species can be recognised in the unopened Petri dish by its broad, velutinous, bluish colonies bearing characteristic, well defined columns of conidia. Growth at 37°C is exceptionally rapid. Conidial heads are also diagnostic: pyriform vesicles bear crowded phialides which bend to be roughly parallel to the stipe axis. Care should be exercised in handling cultures of this species.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
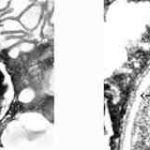
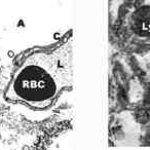
A typical example of a wet mount of a sputum sample from a patient with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis.

-
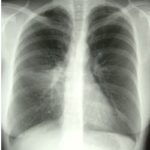
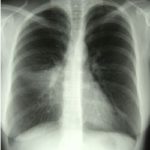
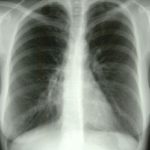
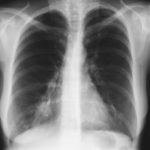
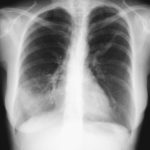
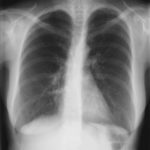
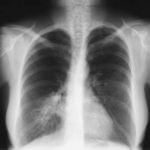
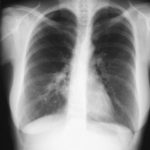
X-Rays -Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) with 3 relapses.
A female patient JO (50 yrs) with right middle lobe collapse. The patient presented with a 6 month history of cough which has persisted despite antibiotics and both steroid and salbutamol inhalers. She then developed acute breathlessness with coughing and wheezing. There was no history of asthma. Bronchoscopy (Image K) showed a mucous plug obstructing the right upper lobe bronchus.
Images D – G are X rays showing relapse in 1998 and recovery
Images H – J are X rays showing relapse in 2003
Image K. Bronchoscopy appearance of mucous impaction of the bronchus intermedius – pt JO (50yrs). There was a long mucous plug in the anterior segment of the RUL. Half of this was aspirated and sent for microscopy and culture. The second half “fell into” the bronchus intermedius (which feeds the right middle lobe) and was only partially aspirated.
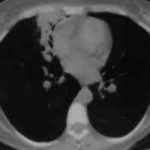
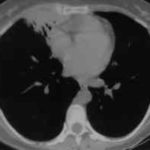
Images L – O: High resolution CT scan of thorax in pt JO, post bronchoscopy. 1.5mm sections at 1 cm intervals of whole lung. There is collapse and consolidation in the right middle lobe with dilation of the right middle lobe bronchi. There is also minor bronchiectasis in the right upperlobe with a little patchy air space shadowing . There is no mediastinal lymphadenopathy or any interstitial fibrosis.
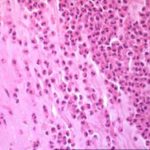
Image P & Q: Histology: Mucous plug (3x 0.5x 0.5cm) containing numerous inflammatory cells, including eosinophils and nuclear debris.GMS staining reveals occasional fungal hyphae with septa and dichotomous branching. These appearances support the diagnosis of bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis. Bronchioalveolar lavage fluid was negative on microscopy and no fungi were grown. A year later Aspergillus fumigatus was grown from her sputum.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 

![Asp[1]fumigatus](https://www.aspergillus.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/Asp1fumigatus.jpg)