Date: 7 May 2013
A four day A. fumigatus culture on malt extract agar (above). Light microscopy pictures are taken at 1000x mag., stained with lacto-phenol cotton blue (right).
Copyright:
With thanks to Niall Hamilton.
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 40-60 mm diam, plane or lightly wrinkled, low, dense and velutinous or with a sparse, floccose overgrowth; mycelium inconspicuous, white; conidial heads borne in a continuous, densely packed layer, Greyish Turquoise to Dark Turquoise (24-25E-F5); clear exudate sometimes produced in small amounts; reverse pale or greenish. Colonies on MEA 40-60 mm diam, similar to those on CYA but less dense and with conidia in duller colours (24-25E-F3); reverse uncoloured or greyish. Colonies on G25N less than 10 mm diam, sometimes only germination, of white mycelium. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies covering the available area, i.e. a whole Petri dish in 2 days from a single point inoculum, of similar appearance to those on CYA at 25°C, but with conidial columns longer and conidia darker, greenish grey to pure grey.
Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, stipes 200-400 µm long, sometimes sinuous, with colourless, thin, smooth walls, enlarging gradually into pyriform vesicles; vesicles 20-30 µm diam, fertile over half or more of the enlarged area, bearing phialides only, the lateral ones characteristically bent so that the tips are approximately parallel to the stipe axis; phialides crowded, 6-8 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, 2.5-3.0 µm diam, with finely roughened or spinose walls, forming radiate heads at first, then well defined columns of conidia.
Distinctive features
This distinctive species can be recognised in the unopened Petri dish by its broad, velutinous, bluish colonies bearing characteristic, well defined columns of conidia. Growth at 37°C is exceptionally rapid. Conidial heads are also diagnostic: pyriform vesicles bear crowded phialides which bend to be roughly parallel to the stipe axis. Care should be exercised in handling cultures of this species.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
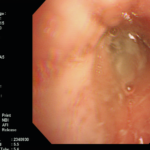
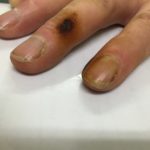
Patient with chronic productive cough, chest pain and ABPA, unable to take itraconazole or nebulised amphotericin B. Smokes at least 40 roll up cigarettes a day.
 ,
, 
-
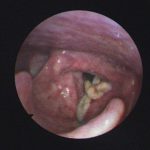
Laryngeal aspergillosis, probably related to inhaled corticosteroids.
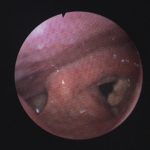 ,
,  ,
, 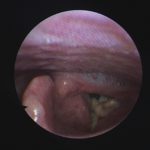 ,
, 
-
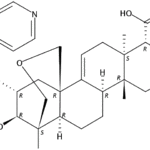
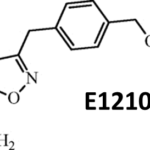
VL-2397 (formerly known as ASP2397) is a novel antifungal drug initially developed by our partner, Astellas Pharma. This drug was isolated from a leaf litter fungus Acremonium species collected in a Malaysian national park. Astellas presented two posters at the 2014 ICAAC meeting which described the in vitro and the in vivo antifungal activities of this drug. The differentiating attributes from the preclinical data of VL-2397 include:
- A novel mechanism of action, with a potential to be complementary or synergistic with the existing classes of antifungals.
- Rapid fungal cell kill activity demonstrated in preclinical models, which was faster than marketed antifungals.
- Activity against azole-resistant fungal species.
- Low propensity for P450 drug-drug interactions.
-
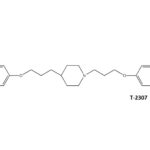
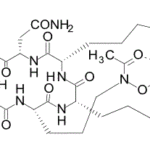
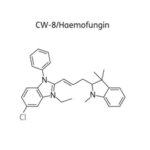
SCY-078, new orally available beta-1,3-d-glucan synthase inhibitor, Formely MK-3118.
-
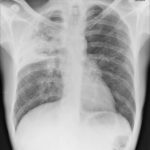
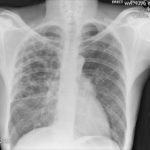
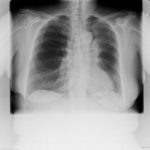
Pt DSM Community acquired primary Aspergillus pneumonia. Two x-rays taken on 02/02/2010 then 05/03/2010
 ,
, 

![Asp[1]fumighead2 Asp[1]fumighead2](https://www.aspergillus.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/Asp1fumighead2.jpg)
 ,
,