Date: 26 November 2013
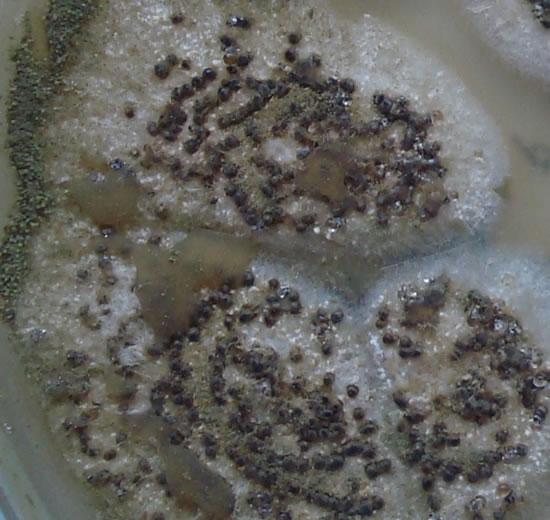
cultures grown from BAL fluid showing formation of sclerotia.
Copyright:
Kindly donated by Dr Claudia Venturelli and Dr Giorgia Bertazzoni, Laboratory of Microbiology – Policlinico of Modena-Italy. © Fungal Research Trust
Notes:
These colonies were isolated from a BAL, (also with bacterial qrowth of S.aureus and S.maltophilia) from a patient with a VAP (undergoing corticosteroid treatment). The growth medium used is sabouraud dextrose agar , incubated at 37° C The identification is made by microscopic/macroscopic observation criteria.
Colonies on CYA 60-70 mm diam, plane, sparse to moderately dense, velutinous in marginal areas at least, often floccose centrally, sometimes deeply so; mycelium only conspicuous in floccose areas, white; conidial heads usually borne uniformly over the whole colony, but sparse or absent in areas of floccose growth or sclerotial production, characteristically Greyish Green to Olive Yellow (1-2B-E5-7), but sometimes pure Yellow (2-3A7-8), becoming greenish in age; sclerotia produced by about 50% of isolates, at first white, becoming deep reddish brown, density varying from inconspicuous to dominating colony appearance and almost entirely suppressing conidial production; exudate sometimes produced, clear, or reddish brown near sclerotia; reverse uncoloured or brown to reddish brown beneath sclerotia. Colonies on MEA 50-70 mm diam, similar to those on CYA although usually less dense. Colonies on G25N 25-40 mm diam, similar to those on CYA or more deeply floccose and with little conidial production, reverse pale to orange or salmon. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies usually 55-65 mm diam, similar to those on CYA at 25°C, but more velutinous, with olive conidia, and sometimes with more abundant sclerotia.
Sclerotia produced by some isolates, at first white, rapidly becoming hard and reddish brown to black, spherical, usually 400- 800 µm diam. Teleomorph not known. Conidiophores borne from subsurface or surface hyphae, stipes 400 µm to 1 mm or more long, colourless or pale brown, rough walled; vesicles spherical, 20-45 µm diam, fertile over three quarters of the surface, typically bearing both metulae and phialides, but in some isolates a proportion or even a majority of heads with phialides alone; metulae and phialides of similar size, 7-10 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, usually 3.5-5.0 µm diam, with relatively thin walls, finely roughened or, rarely, smooth.
Distinctive features
Aspergillus flavus is distinguished by rapid growth at both 25°C and 37°C, and a bright yellow green (or less commonly yellow) conidial colour. A. flavus produces conidia which are rather variable in shape and size, have relatively thin walls, and range from smooth to moderately rough, the majority being finely rough.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
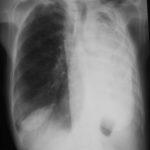
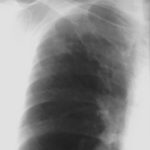
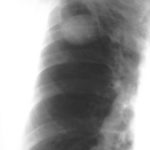
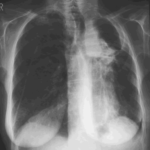
Pt AR Interval development of chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis in the context of sarcoidosis
This patient was diagnosed with sarcoid after developing a chronic cough with the attached chest X-ray. In February 2003 the X-ray demonstrated bilateral extensive changes consistent with fibrocystic sarcoidosis with a complex cavitary area in both apices, more marked on the right. She was given a course of corticosteroids.
-
Further details
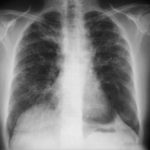
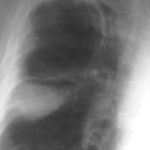
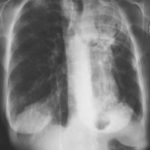
Image B. Additional cavities are apparent inferior to this large cavity and are in communication both with the bronchi and the additional cavities. Some of the apparent cavities are probably dilated bronchi. The left lower lung is completely opacified otherwise. The degree of pleural fibrosis surrounding the left apical cavity is reduced slightly over the interval of four months.
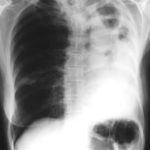
Image C. This shows an almost normal hyperexpanded right lung with a very substantially contracted left lung with one large airway visible and probably incontinuity with a slightly irregular cavity containing some debris, presumably fungal tissue. Other levels show very large left apical cavity with numerous subsections containing debris or fibrotic tissue and almost complete fibrosis of the lung below the level of the carina on the left, with some calcification within the fibrotic lung tissue.
 ,
,  ,
, 
-
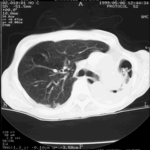
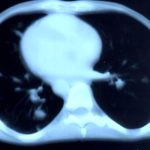
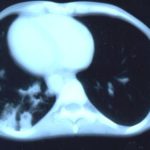
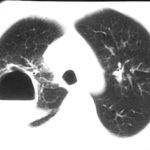
Transverse sections through the thorax of a patient with AIDS, hepatitis C and a left tempero-parietal cerebral lymphoma. His CD4 cell count was 45 x 106 / l. The lymphoma was proven by biopsy after a poor response to anti-toxoplasma therapy. He was given dexamethasone to cover the surgery and then developed diabetes mellitus. He did not receive chemotherapy for his lymphoma but did have 2 cerebral radiotherapy treatments (1.8 Gy each). Three weeks after the biopsy he developed dyspnoea and fever. Shortly after this he developed a right-sided hemiparesis, became comatose and died 2 days later.Autopsy showed a cerebral lymphoma and pulmonary and renal aspergillosis. Aspergillus nidulans was recovered from cultures of lungs and kidney.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
Fever chart of Pt CA -heart transplant pt with candidemia on amphotericin therapy, who developed pulmonary aspergillosis.

-
A Colonies on MEA + 20% sucrose after two weeks; B ascomata, x 40; C conidia and conidiophore, x 920; D ascospores and conidia x2330; E portion of ascoma with asci x920

-
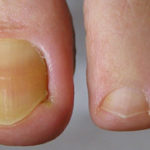
A 66 yr old patient in good general health developed onychomycosis. Samples taken from the affected nail were grown by culture and examined by microscopy. Oral itraconazole pulse therapy was given to the patient (200 mg twice daily for 1 week, with 3 weeks off between successive pulses, for four pulses) and treatment was successful.



 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
,