Date: 26 November 2013
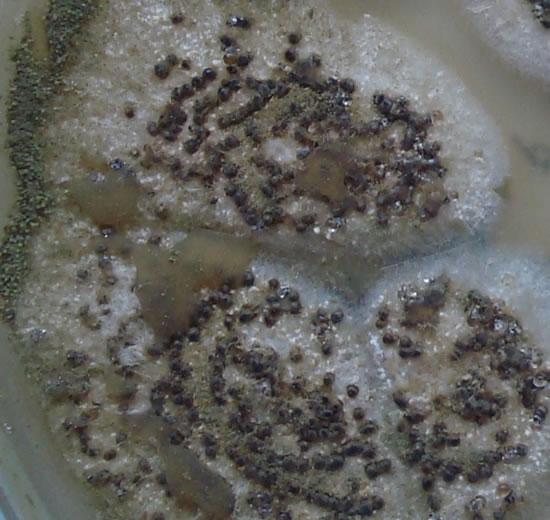
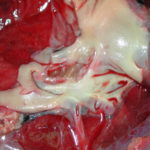
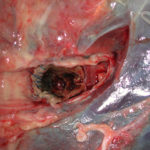
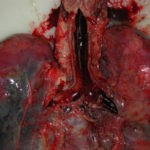
cultures grown from BAL fluid showing formation of sclerotia.
Copyright:
Kindly donated by Dr Claudia Venturelli and Dr Giorgia Bertazzoni, Laboratory of Microbiology – Policlinico of Modena-Italy. © Fungal Research Trust
Notes:
These colonies were isolated from a BAL, (also with bacterial qrowth of S.aureus and S.maltophilia) from a patient with a VAP (undergoing corticosteroid treatment). The growth medium used is sabouraud dextrose agar , incubated at 37° C The identification is made by microscopic/macroscopic observation criteria.
Colonies on CYA 60-70 mm diam, plane, sparse to moderately dense, velutinous in marginal areas at least, often floccose centrally, sometimes deeply so; mycelium only conspicuous in floccose areas, white; conidial heads usually borne uniformly over the whole colony, but sparse or absent in areas of floccose growth or sclerotial production, characteristically Greyish Green to Olive Yellow (1-2B-E5-7), but sometimes pure Yellow (2-3A7-8), becoming greenish in age; sclerotia produced by about 50% of isolates, at first white, becoming deep reddish brown, density varying from inconspicuous to dominating colony appearance and almost entirely suppressing conidial production; exudate sometimes produced, clear, or reddish brown near sclerotia; reverse uncoloured or brown to reddish brown beneath sclerotia. Colonies on MEA 50-70 mm diam, similar to those on CYA although usually less dense. Colonies on G25N 25-40 mm diam, similar to those on CYA or more deeply floccose and with little conidial production, reverse pale to orange or salmon. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies usually 55-65 mm diam, similar to those on CYA at 25°C, but more velutinous, with olive conidia, and sometimes with more abundant sclerotia.
Sclerotia produced by some isolates, at first white, rapidly becoming hard and reddish brown to black, spherical, usually 400- 800 µm diam. Teleomorph not known. Conidiophores borne from subsurface or surface hyphae, stipes 400 µm to 1 mm or more long, colourless or pale brown, rough walled; vesicles spherical, 20-45 µm diam, fertile over three quarters of the surface, typically bearing both metulae and phialides, but in some isolates a proportion or even a majority of heads with phialides alone; metulae and phialides of similar size, 7-10 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, usually 3.5-5.0 µm diam, with relatively thin walls, finely roughened or, rarely, smooth.
Distinctive features
Aspergillus flavus is distinguished by rapid growth at both 25°C and 37°C, and a bright yellow green (or less commonly yellow) conidial colour. A. flavus produces conidia which are rather variable in shape and size, have relatively thin walls, and range from smooth to moderately rough, the majority being finely rough.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
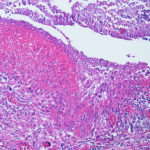
Subacute IPA in rheumatoid nodules of the lung. in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Histology sections stained with H&E
-
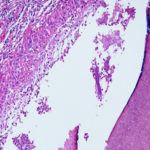
Subacute IPA in rheumatoid nodules of the lung. in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Histology sections stained with H&E.
-
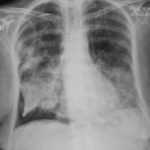
22/09/08 This chest radiograph shows bilateral hazy diffuse airspace disease predominating in the lower lungs with subtle nodularity in upper zones.
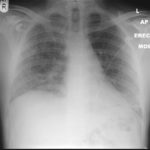
-
Further details
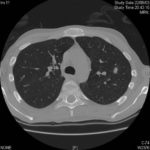
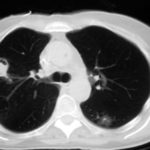
Images 3a,b,c 02/07/07
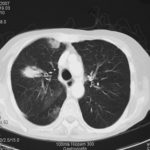
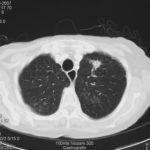
CT thorax, after 2 weeks high dose erythromycin, showing a 2.8cm speculated lesion in the right upper lobe with a further 1.6cm similar mass on the left upper lobe also with a tendency for a central cavitation, and ill defined consolidation involving the peripheral aspect of both upper lobes and to a lesser extent right middle and both lower lobes.History:
A 71 year old woman presents with persistent dry cough. Her second CT scan of thorax shows lesions in the right and left upper lobes with ill defined consolidation in other areas (see images 3a, 3b and 3c). A PET scan is positive. She underwent right thoracotomy and sub-lobar wedge resection. Aspergillus grown from tissue and sputum grows Pseudomonas. Histology confirms the nodule to be non-small cell carcinoma (adenocarcinoma) but other lung areas show organizing pneumonia and another abscess formation with a cluster of branching septate hyphae. Despite starting itraconazole and oral ciprofloxacin she deteriorated with Type 1 respiratory failure. She was intubated and ventilated and switched to intravenous voriconazole and ceftazidime. She developed acute renal failure and then Enterococcus faecium bacteremia and she died 3 days later.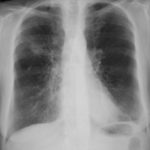 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,