Date: 26 November 2013
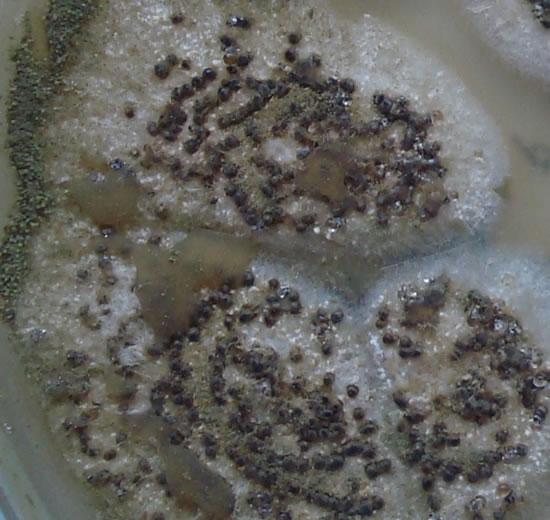
cultures grown from BAL fluid showing formation of sclerotia.
Copyright:
Kindly donated by Dr Claudia Venturelli and Dr Giorgia Bertazzoni, Laboratory of Microbiology – Policlinico of Modena-Italy. © Fungal Research Trust
Notes:
These colonies were isolated from a BAL, (also with bacterial qrowth of S.aureus and S.maltophilia) from a patient with a VAP (undergoing corticosteroid treatment). The growth medium used is sabouraud dextrose agar , incubated at 37° C The identification is made by microscopic/macroscopic observation criteria.
Colonies on CYA 60-70 mm diam, plane, sparse to moderately dense, velutinous in marginal areas at least, often floccose centrally, sometimes deeply so; mycelium only conspicuous in floccose areas, white; conidial heads usually borne uniformly over the whole colony, but sparse or absent in areas of floccose growth or sclerotial production, characteristically Greyish Green to Olive Yellow (1-2B-E5-7), but sometimes pure Yellow (2-3A7-8), becoming greenish in age; sclerotia produced by about 50% of isolates, at first white, becoming deep reddish brown, density varying from inconspicuous to dominating colony appearance and almost entirely suppressing conidial production; exudate sometimes produced, clear, or reddish brown near sclerotia; reverse uncoloured or brown to reddish brown beneath sclerotia. Colonies on MEA 50-70 mm diam, similar to those on CYA although usually less dense. Colonies on G25N 25-40 mm diam, similar to those on CYA or more deeply floccose and with little conidial production, reverse pale to orange or salmon. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies usually 55-65 mm diam, similar to those on CYA at 25°C, but more velutinous, with olive conidia, and sometimes with more abundant sclerotia.
Sclerotia produced by some isolates, at first white, rapidly becoming hard and reddish brown to black, spherical, usually 400- 800 µm diam. Teleomorph not known. Conidiophores borne from subsurface or surface hyphae, stipes 400 µm to 1 mm or more long, colourless or pale brown, rough walled; vesicles spherical, 20-45 µm diam, fertile over three quarters of the surface, typically bearing both metulae and phialides, but in some isolates a proportion or even a majority of heads with phialides alone; metulae and phialides of similar size, 7-10 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, usually 3.5-5.0 µm diam, with relatively thin walls, finely roughened or, rarely, smooth.
Distinctive features
Aspergillus flavus is distinguished by rapid growth at both 25°C and 37°C, and a bright yellow green (or less commonly yellow) conidial colour. A. flavus produces conidia which are rather variable in shape and size, have relatively thin walls, and range from smooth to moderately rough, the majority being finely rough.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
This 24-year-old male with AML on chemotherapy developed recent onset fever and cough. B- Representative section of High Resolution CT shows centri-lobular nodules, ‘tree-in-bud’ appearance consistent with bronchogenic spread of disease.

-
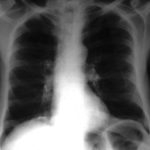
This 24-year-old male with AML on chemotherapy developed recent onset fever and cough. A: Chest radiograph showing patchy air space consolidation involving both lungs.
-
This man with severe chronic fibrosing alveolitis underwent a single left lung transplant at the end of November 2004. Postoperatively he developed reperfusion pulmonary oedema and was difficult to ventilate. He also developed acute renal failure requiring haemodialysis/haemofiltration which corrected his fluid overload and rising creatinine.Rejection was prevented with cyclosporin, mycophenolate and a decreasing dose of methylprednisolone. Cardiovascular problems identified mild pulmonary anastomostic stenosis with a 5% pressure gradient. He had a tracheostomy about 12 days post transplant. He then developed episodes of hypoxia and increased ventilatory pressures. Several bronchoscopies showed mucus plugging in the trachea and major bronchi. These were aspirated, with improvement of oxygenation. Cultures of one of these plugs grew A. fumigatus. These images show a bronchoscopy view of the trachea and anastomosis. Major obstruction of the airway is visible (70%) distal to the anastomosis which looks healthy. Some evidence of tracheal inflammation is visible.
 ,
, 
-
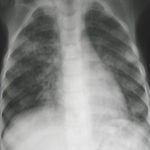
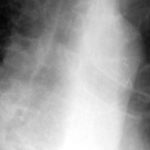
The chest x-ray shows a patient who had a left lung transplanted in May 2003 for cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis, which was diagnosed post-transplant as sarcoidosis.
-
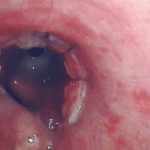
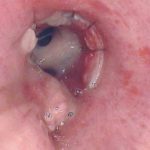
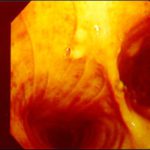
Tracheal aspergillosis. Bronchoscopic views of the trachea showing nodules in the trachea that revealed Aspergillus on biopsy. The patient had chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with fludarabine and corticosteroids and presented with wheezing and bilateral alveolar shadows.

-
Tracheal aspergillosis, Bronchoscopic views of the trachea showing nodules in the trachea that revealed Aspergillus on biopsy. The patient had chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with fludarabine and corticosteroids and presented with wheezing and bilateral alveolar shadows.

-
Tracheal aspergillosis. Bronchoscopic views of the trachea showing nodules in the trachea that revealed Aspergillus on biopsy. The patient had chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with fludarabine and corticosteroids and presented with wheezing and bilateral alveolar shadows.
-
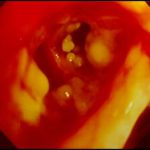
Tracheal aspergillosis. Bronchoscopic views of the trachea showing nodules in the trachea that revealed Aspergillus on biopsy. The patient had chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with fludarabine and corticosteroids and presented with wheezing and bilateral alveolar shadows.
-
Aspergillus tracheobronchitis in a normal child. This figure, drawn in 1890, illustrates the appearances of the trachea and main bronchi at autopsy in a 3 year old child. She had little else wrong at autopsy other than a minor degree of tuberculosis. She is the first recorded case of Aspergillus tracheobronchitis in the literature and illustrates well that this disease can affect previously well non-inimmunocompromised people. The full case is reported in Wheaton SW.

-
pt FT. Normal chest radiograph of patient with extensive pseudomembranous Aspergillus tracheobronchitis, 4 days before death.