Date: 26 November 2013
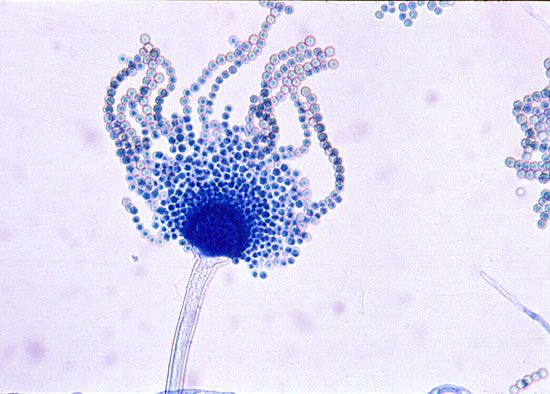
Microscopic morphology of A. flavus. Conidial heads are radiate, splitting to form loose columns, biseriate but having some heads with phialides borne directly on the vesicle.
Copyright:
With thanks to G Kaminski. D Ellis and R Hermanis Mycology Unit Women’s & Children’s Hospital , Adelaide, South Australia 5006. © Fungal Research Trust
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 60-70 mm diam, plane, sparse to moderately dense, velutinous in marginal areas at least, often floccose centrally, sometimes deeply so; mycelium only conspicuous in floccose areas, white; conidial heads usually borne uniformly over the whole colony, but sparse or absent in areas of floccose growth or sclerotial production, characteristically Greyish Green to Olive Yellow (1-2B-E5-7), but sometimes pure Yellow (2-3A7-8), becoming greenish in age; sclerotia produced by about 50% of isolates, at first white, becoming deep reddish brown, density varying from inconspicuous to dominating colony appearance and almost entirely suppressing conidial production; exudate sometimes produced, clear, or reddish brown near sclerotia; reverse uncoloured or brown to reddish brown beneath sclerotia. Colonies on MEA 50-70 mm diam, similar to those on CYA although usually less dense. Colonies on G25N 25-40 mm diam, similar to those on CYA or more deeply floccose and with little conidial production, reverse pale to orange or salmon. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies usually 55-65 mm diam, similar to those on CYA at 25°C, but more velutinous, with olive conidia, and sometimes with more abundant sclerotia.
Sclerotia produced by some isolates, at first white, rapidly becoming hard and reddish brown to black, spherical, usually 400- 800 µm diam. Teleomorph not known. Conidiophores borne from subsurface or surface hyphae, stipes 400 µm to 1 mm or more long, colourless or pale brown, rough walled; vesicles spherical, 20-45 µm diam, fertile over three quarters of the surface, typically bearing both metulae and phialides, but in some isolates a proportion or even a majority of heads with phialides alone; metulae and phialides of similar size, 7-10 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, usually 3.5-5.0 µm diam, with relatively thin walls, finely roughened or, rarely, smooth.
Distinctive features
Aspergillus flavus is distinguished by rapid growth at both 25°C and 37°C, and a bright yellow green (or less commonly yellow) conidial colour. A. flavus produces conidia which are rather variable in shape and size, have relatively thin walls, and range from smooth to moderately rough, the majority being finely rough.
Images library
-
Title
Legend