Date: 26 November 2013
X-Rays -Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) with 3 relapses.
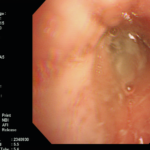
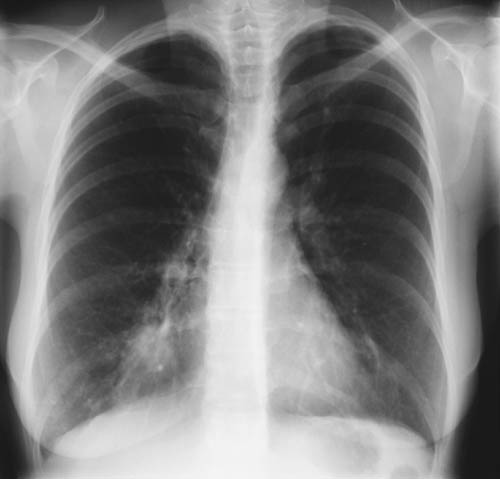
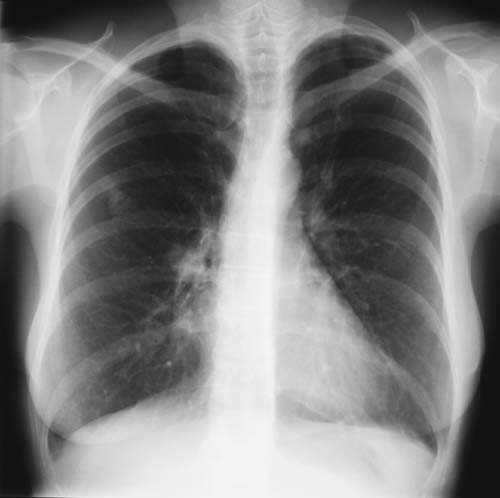
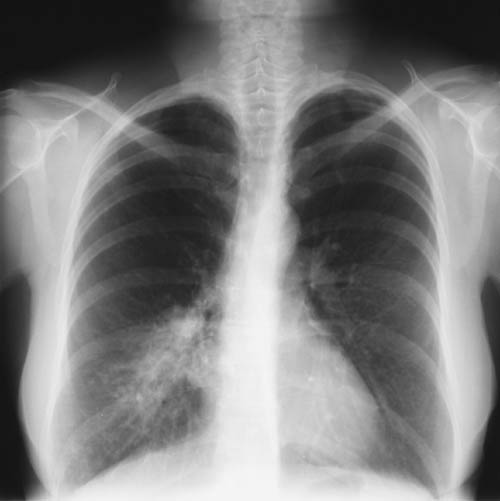
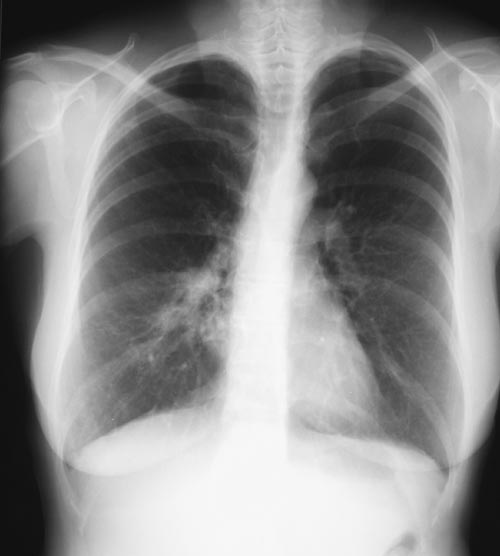
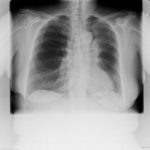
A female patient JO (50 yrs) with right middle lobe collapse. The patient presented with a 6 month history of cough which has persisted despite antibiotics and both steroid and salbutamol inhalers. She then developed acute breathlessness with coughing and wheezing. There was no history of asthma. Bronchoscopy (Image K) showed a mucous plug obstructing the right upper lobe bronchus.
Images D – G are X rays showing relapse in 1998 and recovery
Images H – J are X rays showing relapse in 2003
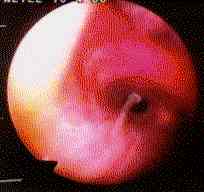
Image K. Bronchoscopy appearance of mucous impaction of the bronchus intermedius – pt JO (50yrs). There was a long mucous plug in the anterior segment of the RUL. Half of this was aspirated and sent for microscopy and culture. The second half “fell into” the bronchus intermedius (which feeds the right middle lobe) and was only partially aspirated.
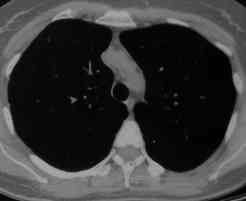
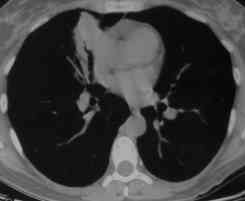
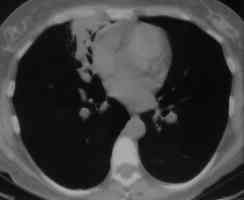
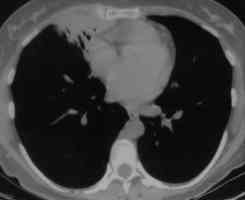
Images L – O: High resolution CT scan of thorax in pt JO, post bronchoscopy. 1.5mm sections at 1 cm intervals of whole lung. There is collapse and consolidation in the right middle lobe with dilation of the right middle lobe bronchi. There is also minor bronchiectasis in the right upperlobe with a little patchy air space shadowing . There is no mediastinal lymphadenopathy or any interstitial fibrosis.
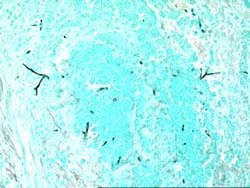
Image P & Q: Histology: Mucous plug (3x 0.5x 0.5cm) containing numerous inflammatory cells, including eosinophils and nuclear debris.GMS staining reveals occasional fungal hyphae with septa and dichotomous branching. These appearances support the diagnosis of bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis. Bronchioalveolar lavage fluid was negative on microscopy and no fungi were grown. A year later Aspergillus fumigatus was grown from her sputum.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
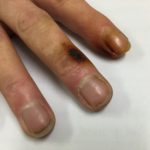
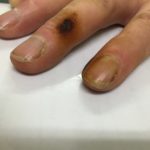
Patient with chronic productive cough, chest pain and ABPA, unable to take itraconazole or nebulised amphotericin B. Smokes at least 40 roll up cigarettes a day.
 ,
, 
-
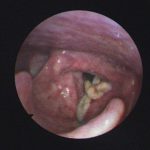
Laryngeal aspergillosis, probably related to inhaled corticosteroids.
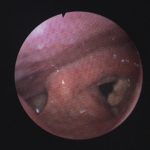 ,
,  ,
, 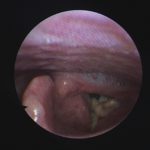 ,
, 
-
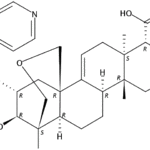
VL-2397 (formerly known as ASP2397) is a novel antifungal drug initially developed by our partner, Astellas Pharma. This drug was isolated from a leaf litter fungus Acremonium species collected in a Malaysian national park. Astellas presented two posters at the 2014 ICAAC meeting which described the in vitro and the in vivo antifungal activities of this drug. The differentiating attributes from the preclinical data of VL-2397 include:
- A novel mechanism of action, with a potential to be complementary or synergistic with the existing classes of antifungals.
- Rapid fungal cell kill activity demonstrated in preclinical models, which was faster than marketed antifungals.
- Activity against azole-resistant fungal species.
- Low propensity for P450 drug-drug interactions.
-
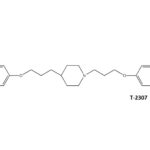
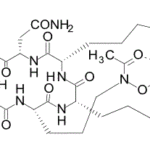
SCY-078, new orally available beta-1,3-d-glucan synthase inhibitor, Formely MK-3118.
-
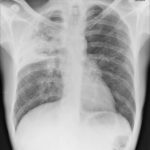
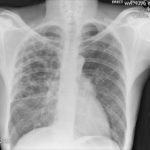
Pt DSM Community acquired primary Aspergillus pneumonia. Two x-rays taken on 02/02/2010 then 05/03/2010
 ,
, 








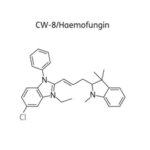
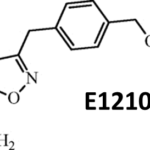
 ,
,