Lecture Overview
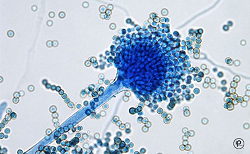
In his first lecture, Dustin explains that adaptive immunity allows an individual to specifically recognize and respond to a vast number of molecules. B cells recognize intact antigens and produce neutralizing antibodies. T cells, on the other hand, have receptors on their surface that recognize very small antigen fragments bound to MHC on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APC). Dustin explains that T cells overcome the challenges of finding and binding to the APCs with the help of a multitude of adhesion molecules. Once the T cell receptor has bound a peptide antigen, an immunological synapse, with its typical bulls-eye structure, is formed resulting in T cell activation.
In Part 2, Dustin describes how a reconstituted system has allowed the immunological synapse to be studied in molecular detail. It is possible to visualize the localization of signaling molecules such as kinases, and determine the role of the actin cytoskeleton in regulating this localization. Dustin also touches on the role of the immunological synapse in autoimmune disease and cancer.
In his last lecture, Dustin presents work from his lab showing that T cell receptor enriched vesicles are generated in the immunological synapse. These vesicles can be transferred to B cells leading to activation of the B cells and, potentially, the production of higher specificity antibodies.
Speaker Bio
Michael Dustin is Professor of Immunology and Director of Research at The Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology at the University of Oxford. Prior to joining the Kennedy Institute, Dustin was a faculty member at the Skirball Institute of Biomolecular Medicine at New York University from 2001-2013 and at Washington University School of Medicine from 1993-2000. Dustin received his BA in Biology from Boston University and his PhD in Cell and Developmental Biology from Harvard University.
As described in his iBioSeminar, Dustin’s lab studies the molecular events that take place at the immunological synapse. Future research will focus on developing therapies targeted to the immunological synapse to cure chronic inflammatory illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Dustin is an active participant in the immunology community; he is a member of numerous grant review committees and journal editorial boards. His research has been recognized with many awards including the 2000 Presidential Early Career Award in Science and Engineering and the 2012 DART-NYU Biotechnology Achievement Award.
Medical and Patient education videos
-
Title
Description
-

Powerpoint presentation December 2009
-

Published on 23 Apr 2014.
Wild Type A. fumigatus strain differences and antifungal susceptibility in Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis
-

Published on 18 Jun 2014 CT scan image of a dog with Nasal Aspergillosis
-
Uploaded on 11 Feb 2012 Dr. Sunena Argo discusses the diagnosis and management of ABPA
-

Uploaded on 12 Feb 2012 Dr. Heather Doss reviews the diagnosis and management of ABPA. Held on Oct 17, 2011.
-

Published on 28 Dec 2012 Developed and produced for http://www.MechanismsinMedicine.com Animation Description: One of the most lethal complications of invasive aspergillosis is dissemination to the brain. The diagnosis is difficult and it has been associated with near 100% mortality, however aggressive antifungal therapy can improve outcomes. Watch this animation for more information.
-

“With every breath you take, you are inhaling a potentially deadly pathogen. You can’t see this parasite floating into your nostrils and weaving its way down into your lungs. You probably breathe many of them right back out again, but some stick with every breath. If you’re a healthy non-smoker, have no fear, your immune system has an excellent chance of destroying the invaders before they can make you sick. If your lungs or immune system are compromised, you still have an excellent chance of escaping these frequent attacks unscathed. But, for the unlucky few among us, the fungal pathogen Aspergillus might just win. Let’s take a closer look and see what we could be in for.”

An online science educational resource – intended for students but is suitable for the layperson.
Requires registration for a free trial.