Description:
Fungi Exploitation
Science is going back to basics …We look at how more than 28,000 strains of fungus held in the UK’s national collection are becoming the focus of research seeking new antibacterial drugs. The collection has great roots – it still holds an original sample of Sir Alexander Fleming’s penicillin. Quentin Cooper is joined by Dr Joan Kelley, Executive Director Bioservices, CABI and Professor Peter Bramley, Head of the School of Biological Sciences Royal Holloway, University of London.
Fungi Exploitation – Electron Microscopes
February 2008 BBC Radio 4
Medical and Patient education videos
-
Title
Description
-
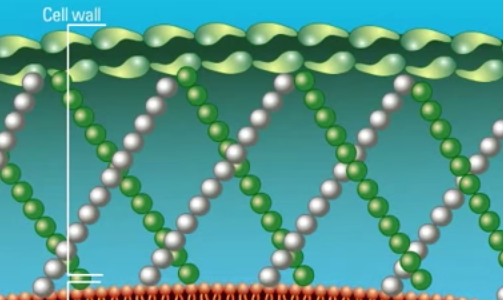
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane. Watch this animation for more information.
-

Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and are not related to bacteria. As eukaryotes, they contain membrane bound organelles and possess a cell membrane surrounded by a rigid cell wall. Watch this animation for more information on the unique structural properties of fungi.
-
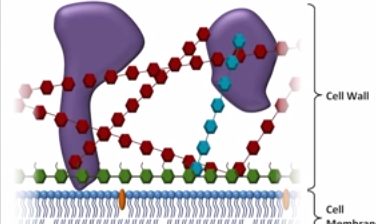
A review of antifungals, focusing on amphotericin B, azoles, and echinocandins. Structure, mechanism, spectrum of antifungal activity, common clinical uses, and common side effects/toxicities are all discussed. (April 2015)
-
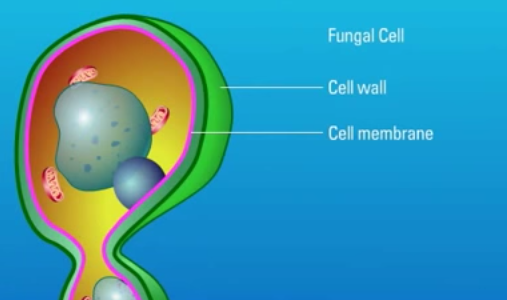
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane.
-
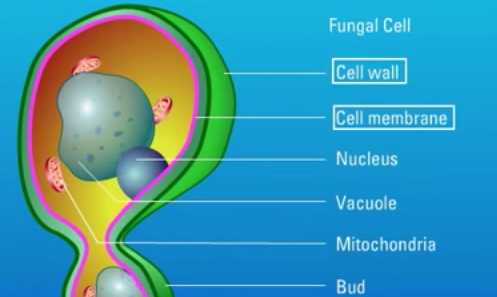
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane.
-
Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
-

Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
-

Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
