ID 2: 597
Toxin: y
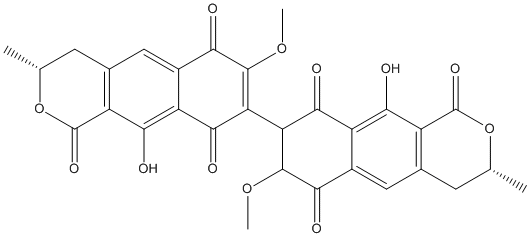
Systematic name:
(8,8′-Bi-1H-naphtho(1,2-c)pyran)-1,1′,7,7′,10,10′-hexone, 3,3′,4,4′-tetrahydro-6,6′-dihydroxy-9,9′-dimethoxy-3,3′-dimethyl-, (3R,3’R)- (8CI)
(8,8′-BI-1H-NAPHTHO(2,3-c)PYRAN)-1,1′,6,6′,9,9′-HEXONE, 3,3′,4,4′-TETRAHYDRO-10,
(8,8′-Bi-1H-naphtho(2,3-c)pyran
Molecular formulae:
C30H22O12
Molecular weight: 574.488
Chemical abstract number: 1685-91-2
Chemical type: Dihydroisocoumarin
Literature reference:
References URL:
Aspergillus Species known to produce this metabolite:
Toxicity:
Doses of 448 mg/kg body-weight in mice caused symptoms of liver damage including jaundice, necrotising cholangitis and other histological alterations.
Robbers JE, Hong S, Tuite J, Carlton WW. Production of xanthomegnin and viomellein by species of Aspergillus correlated with mycotoxicosis produced in mice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):819-23.
Structure image:
Date uploaded: 2008-07-14 11:13:57
Mycotoxin & Metabolites
-
Metabolite
Produced by (species)
Molecular weight
References
-
399.0
428.5
445.5
443.5
321.5
138.1
264.3
138.1
182.2
Mycotoxin & Metabolite database
Aspergillus species produce a large number of secondary metabolites, sometimes referred to as extrolites. We attempt to list them all here and we also collect published papers.
Search Metabolite papers here
