ID 2: 508
Toxin: y
Trivial name:
Helvolic acid (6CI,7CI); (Z)-6β,16β-Dihydroxy-3,7-dioxo-29-nor-8α,9β,13α,14β-dammara-1,17(20),24-trien-21-oic acid diacetate; Fumigacin; NSC 319943
Systematic name:
29-Nordammara-1,17(20),24-trien-21-oic acid, 6,16-bis(acetyloxy)-3,7-dioxo-, (4a,6b,8a,9b,13a,14b,16b,17Z)- (9CI)
Molecular formulae:
C33H44O8
Molecular weight: 568.70
Chemical abstract number: 29400-42-8
Literature reference:
References URL:
Aspergillus Species known to produce this metabolite:
Toxicity:
mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 400mg/kg (400mg/kg) “Antibiotics: Origin, Nature, and Properties,” Korzyoski, T., et al., eds., Washington, DC, American Soc. for Microbiology, 1978Vol. 3, Pg. 1837, 1978.
mouse LDLo intravenous 500mg/kg (500mg/kg) “Antibiotics: Origin, Nature, and Properties,” Korzyoski, T., et al., eds., Washington, DC, American Soc. for Microbiology, 1978Vol. 3, Pg. 1837, 1978.
Structure image:
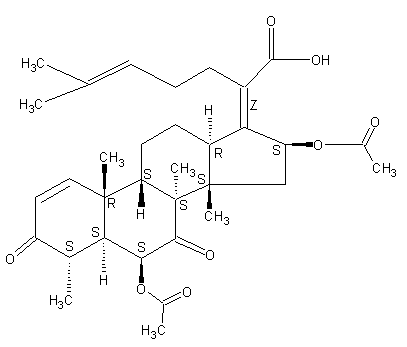
Date uploaded: 2008-01-25 00:53:58
Mycotoxin & Metabolites
-
Metabolite
Produced by (species)
Molecular weight
References
Mycotoxin & Metabolite database
Aspergillus species produce a large number of secondary metabolites, sometimes referred to as extrolites. We attempt to list them all here and we also collect published papers.
