ID 2: 214
Toxin: y
Trivial name:
Anthraquinone, 1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methyl- (8CI); 1,3,8-Trihydroxy-6-methyl-9,10-anthraquinone; 1,3,8-Trihydroxy-6-methylanthraquinone; 1,6,8-Trihydroxy-3-methylanthraquinone; 3-Methyl-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone; 4,5,7-Trihydroxy-2-methylanthraquinone; Archin; Emodin; Emodol; Frangula emodin; Frangulic acid; NSC 408120; NSC 622947; Rheum emodin; Schuttgelb
Systematic name:
9,10-Anthracenedione, 1,3,8-trihydroxy-6-methyl- (9CI)
Molecular formulae:
C15H10O5
Molecular weight: 270.24
Chemical abstract number: 518-82-1
Literature reference:
References URL:
Aspergillus Species known to produce this metabolite:
Toxicity:
Mean lethal dose of emodin orally administered to 1-day-old DeKalb cockerels was 3.7 mg/kg.
BACKGROUND: Emodin, a widely available herbal remedy, was evaluated for potential effects on pregnancy outcome. METHODS: Emodin was administered in feed to timed-mated Sprague-Dawley (CD) rats (0, 425, 850, and 1700 ppm; gestational day [GD] 6-20), and Swiss Albino (CD-1) mice (0, 600, 2500 or 6000 ppm; GD 6-17). Ingested dose was 0, 31, 57, and approximately 80-144 mg emodin/kg/day (rats) and 0, 94, 391, and 1005 mg emodin/kg/day (mice). Timed-mated animals (23-25/group) were monitored for body weight, feed/water consumption, and clinical signs. At termination (rats: GD 20; mice: GD 17), confirmed pregnant dams (21-25/group) were evaluated for clinical signs: body, liver, kidney, and gravid uterine weights, uterine contents, and number of corpora lutea. Fetuses were weighed, sexed, and examined for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations/variations. RESULTS: There were no maternal deaths. In rats, maternal body weight, weight gain during treatment, and corrected weight gain exhibited a decreasing trend. Maternal body weight gain during treatment was significantly reduced at the high dose. In mice, maternal body weight and weight gain was decreased at the high dose. CONCLUSIONS: Prenatal mortality, live litter size, fetal sex ratio, and morphological development were unaffected in both rats and mice. At the high dose, rat average fetal body weight per litter was unaffected, but was significantly reduced in mice. The rat maternal lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL) was 1700 ppm; the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) was 850 ppm. The rat developmental toxicity NOAEL was > or =1700 ppm. A LOAEL was not established. In mice, the maternal toxicity LOAEL was 6000 ppm and the NOAEL was 2500 ppm. The developmental toxicity LOAEL was 6000 ppm (reduced fetal body weight) and the NOAEL was 2500 ppm. Copyright 2004 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Structure image:
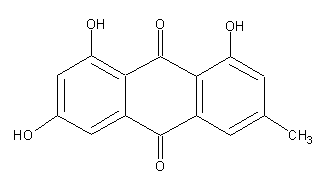
Date uploaded: 2007-06-09 16:01:14
Mycotoxin & Metabolites
-
Metabolite
Produced by (species)
Molecular weight
References
-
399.0
428.5
445.5
443.5
321.5
138.1
264.3
138.1
182.2
Mycotoxin & Metabolite database
Aspergillus species produce a large number of secondary metabolites, sometimes referred to as extrolites. We attempt to list them all here and we also collect published papers.
Search Metabolite papers here
