ID 2: 162
Toxin: y
Systematic name:
Cyclopenta[c]furo[3′,2′:4,5]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-1,11-dione, 2,3,6a,9a-tetrahydro-4-methoxy-, (6aR-cis)-
Molecular formulae:
C17H12O6
Molecular weight: 312.3
Chemical abstract number: 1162-65-8
Chemical type: Dihydrodifuranocoumarin
Literature reference:
References URL:
Aspergillus Species known to produce this metabolite:
Toxicity:
Primarily an hepatotoxin and in some species, such as the rat and the rainbow trout, an hepatocarcinogen and mutagen. Toxic response depends on how the molecule is metabolised in the liver. Oral LD50 for adult male rat 7.2 mg/kg, adult dog 0.5 mg/kg and day-old duckling 0.35 mg/kg body-weight, respectively. Possibly associated with human liver cancer in association with hepatitis B infection.
Structure image:
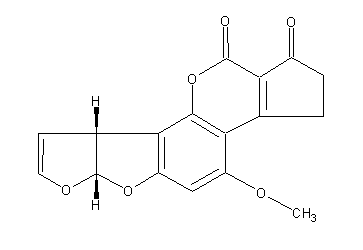
Date uploaded: 2008-07-07 13:06:04
Mycotoxin & Metabolites
-
Metabolite
Produced by (species)
Molecular weight
References
-
484
468
386
384.3
180.2
428.7
322.3
382.4
396.4
Mycotoxin & Metabolite database
Aspergillus species produce a large number of secondary metabolites, sometimes referred to as extrolites. We attempt to list them all here and we also collect published papers.
Search Metabolite papers here
