Submitted by GAtherton on 25 April 2017
The 27th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) has seen the presentation of a series of papers on a new antifungal drug that is entirely novel in action and thus should be useful against fungi that are already resistant to other antifungal drugs.
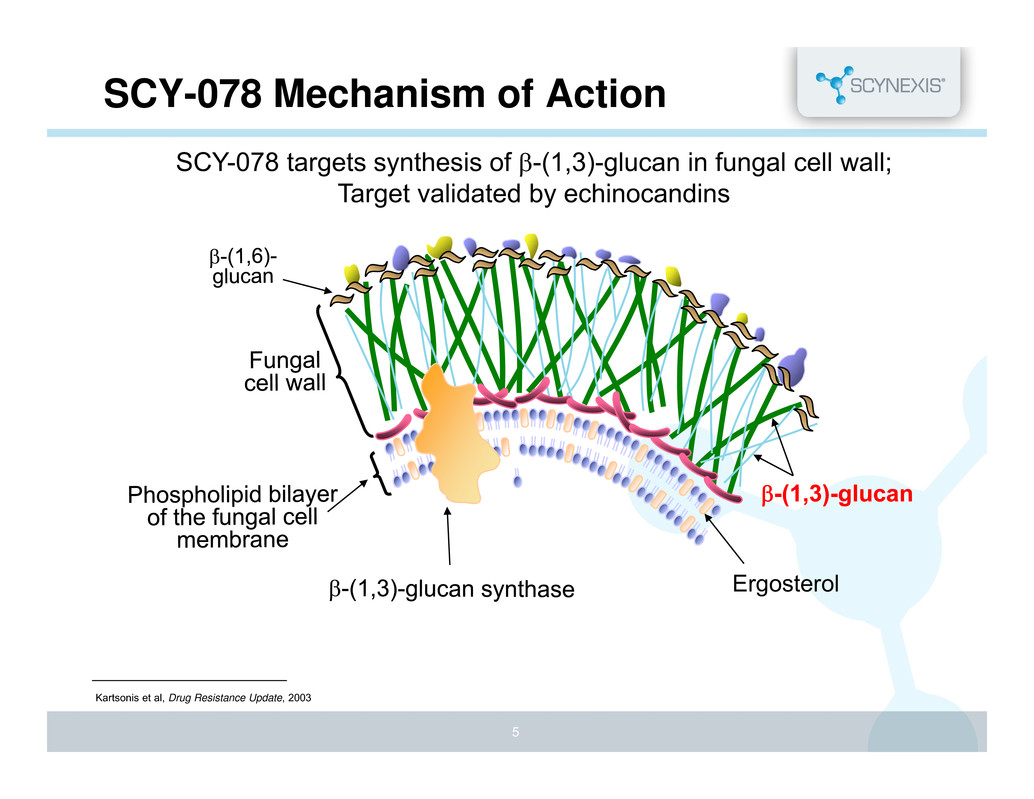
SCY-078 is a glucan synthase inhibitor effective against Aspergillus and Candida species which has already been shown to be safe and effective with adequate systemic doses being achieved via oral and IV routes of administration. The latest reports of subsequent phase 2 trials showed that SCY-078 is equivalent in efficacy to standard-of-care drugs for the treament of Candidiasis and was effective against strains of Candida that were already resistant to existing antifungal drugs.
Long et. al. reported at ECCMID on the use of SCY-078 in combination with three different antifungal drugs; Isavuconazole, Voriconazole and Amphotericin B. The minimal inhibitory concentration’s (MIC) of strains of Aspergillus fumigatus were determined including strains that are resistant to azole antifungal drugs. In all three cases combination with SCY-078 was effective against all strains of A fumigatus, including those resistant to azole drugs.
Interestingly in all three cases there was a synergistic interaction between SCY-078 and its partner such that in combination they were far more effective (lower MIC) than was expected given the addition of the two. This suggests that the use of SCY-078 in combination with other azole or Amphotericin drugs enhances the efficacy of both and may give doctors a new, powerful treatment option for use especially when an infecting strain of A fumigatus has become resistant to current azole drugs.
A collection of articles on the development of SCY-078
News archives
-
Title
Date