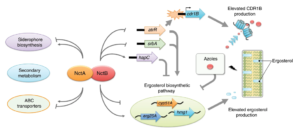
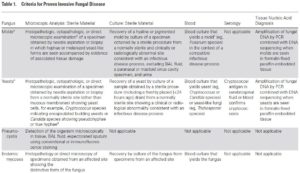
Submitted by Aspergillus Administrator on 30 April 2020
Influenza can be complicated by invasive aspergillosis, as first described in 1952. About 35% of critically ill patients with COVID-19 are treated with corticosteroids and we know from meta-analyses that these patients have nearly double the mortality, lower ICU stay and more secondary infections, probably including aspergillosis (Rodrigo et al., 2015 and Ni et al., 2019). This link with corticosteroids is likely with COVID-19. Aspergillus antigen testing of respiratory fluids should be routine for these very ill patients.
Research into COVID-19 is taking place at an incredible pace but there is still much we don’t know. One key unknown is the frequency and impact of co-infections. Gangneux et al. highlights the fact that invasive fungal infections are still rarely reported and may be underdiagnosed. It reports what is not known and what should be done.
Studies are starting to emerge reporting fungal co-infection rates. Koehler et al. published this week that clinicians caring for patients with ARDS due to COVID-19 should consider invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and subject respiratory samples to comprehensive analysis to detect co-infection. They noted that five of 19 critically ill patients (26%) developed COVID-19 associated invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. A pre-published report from Alanio et al. found putative IPA in almost one third of successive critically ill COVID-19 patients (not yet peer-reviewed). A further early release article describes a fatal case of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in an immunocompetent patient in France who had severe coronavirus disease–associated pneumonia (Blaize et al., 2020).
As further research is undertaken we will collate it and make it available on the LIFE Worldwide website. The page will be updated as more information becomes available.
News archives
-
Title
Date


 ,
,  ,
,